May 20, 2021
New progress in cancer chemotherapy immunotherapy based on small molecule drugs
Professor Youqing Shen’s group of College of Chemical and Biological Engineering at Zhejiang University has made an important progress in cancer chemotherapy immunotherapy based on small molecule drugs. The related research results are entitled Co-delivery of IOX1 and doxorubicin for antibody-independent cancer chemo-immunotherapy , which was published online in Nature Communications on April 23, 2021.

Team members found a histone demethylase inhibitor, 5-carboxyl-8-hydroxyquinoline (IOX1), which can inhibit the histone demethylase JMJD1A of cancer cells and down regulate the expression of JMJD1A β- Catenin, which reduces the expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), can inhibit the growth of many tumor models by binding with DOX. IOX1 provides an effective example of antibody free chemotherapy immunotherapy for cancer treatment.
In addition, Prof. Youqing Shen's group published a research paper entitled Enhanced tumour penetration and prolonged circulationin blood of polyzwitterion–drug conjugates with cell-membrane affinity online in Nature Biomedical Engineering together with other research groups on April 15, 2021.This paper provides a new idea for the design of clinical translational nanodrugs.
In recent years, many significant advances have been made in the field of cancer immunotherapy, especially the immune checkpoint blocking therapy (ICB) for programmed death-1 (PD-1) / programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), which has greatly improved the therapeutic effect of cancer. Blocking PD-1 / PD-L1 interaction with antibody can restore the normal function of T lymphocytes. However, due to the poor penetration of antibodies and the highly immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, ICB therapy is ineffective in about 40% of melanoma and solid tumors.
Therefore, scientists have explored ways to improve the prognosis of PD-1 / PD-L1 antibody therapy by alleviating the immunosuppressive microenvironment. For example, some chemotherapeutic drugs (such as DOX) can induce the immunogenic death (ICD) of tumor cells, release damps, and promote the transfer of tumor associated antigens to dendritic cells (DCS), thus activating the maturation of DCS and the infiltration of T cells and memory T cells in tumor tissues, it turns immunosuppressive tumors into immunoreactive tumors.
Different stages of clinical trials have shown the benefits of chemotherapy combined with ICB immunotherapy. In this combination therapy, low-dose or standard dose chemotherapy is mostly used to avoid chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression and damage to the host immune system. However, how to effectively induce ICD at low dose, especially in drug-resistant cancer cells, is the key to effective chemotherapy immunotherapy.
Another key problem to improve the efficacy of ICB immunotherapy is to improve the blocking efficiency of PD-1 / PD-L1. Because of the poor penetration of antibody, the blocking efficiency is usually limited.
In this study, researchers found an efficient immunotherapeutic small molecule, 5-carboxyl-8-hydroxyquinoline (IOX1), which can reduce the growth of various tumor models by binding with DOX(Fig. 1). IOX1 can not only effectively down regulate the expression of PD-L1, but also inhibit the multidrug resistance of cancer cells, promote the accumulation of DOX in cells, and greatly enhance the DOX induced ICD.
In the mouse model, the combination of IOX1 and DOX liposomes (IPLD) greatly promoted the infiltration and activity of T cells(Fig. 3a), and significantly reduced the immunosuppressive factors of tumor. In a variety of tumor bearing mouse models, IOX1 showed excellent antitumor activity. It could clear not only small tumors with initial tumor size of 80 mm3, but also large tumors with initial tumor size of 350 mm3, it can produce long-term immune memory and resist the re invasion of subcutaneous and lung metastases.
|
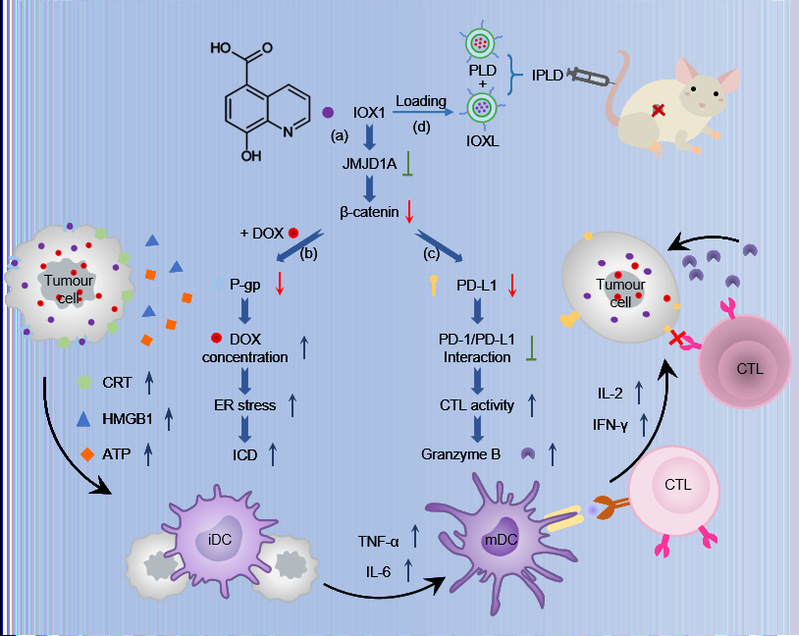
Figure 1: mechanism of IOX1 enhancing chemotherapy immunotherapy
(a) IOX1 inhibits JMJD1A and down regulates its downstream β- Expression of catenin
(b) IOX1 down regulated P-gp, increased DOX concentration in tumor cells and promoted immunogenic cell death
(c) IOX1 down regulates the expression of PD-L1 in tumor cells and destroys PD-1 / PD-L1 signal axis
(d) The synergistic effect of these two effects makes the combination of IOX1 and PEGylated DOX liposomes can inhibit the growth of many kinds of tumors.
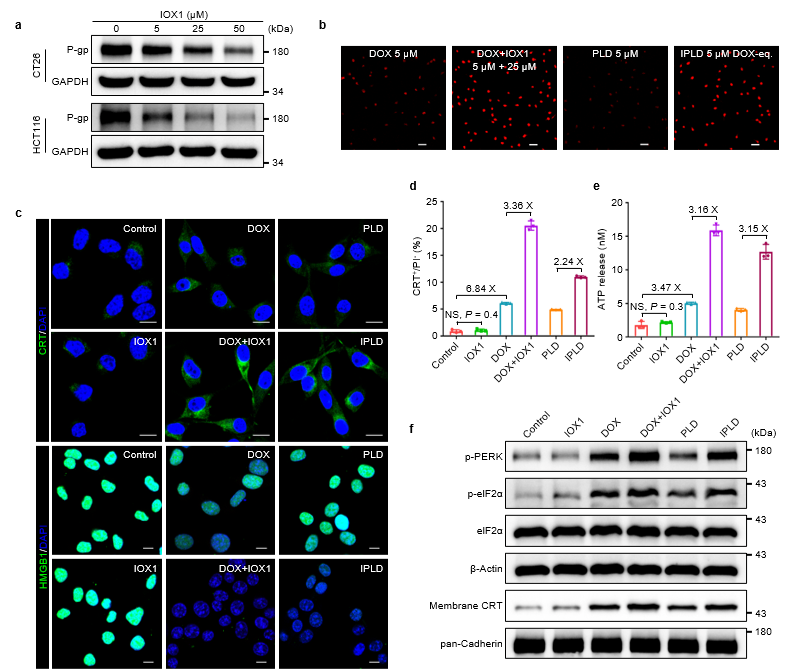
Figure 2: IOX1 inhibits drug resistance and enhances doxorubicin mediated ICD
(a) Western blot showed that IOX1 decreased the expression of P-gp in tumor cells
(b) Fluorescence images showed that IOX1 increased the concentration of DOX in tumor cells
(c) Immunofluorescence showed that IOX1 increased DOX mediated CRT eversion and HMGB1 release
(d) Flow cytometry showed that IOX1 increased DOX mediated CRT membrane ectopia
(e) The ATP assay kit showed that IOX1 increased DOX mediated ATP efflux
(f) Western blot analysis showed that IOX1 enhanced the endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by DOX, thereby enhancing the membrane protein level of CRT.

Figure 3: IOX1 reduces PD-L1 level of tumor, promotes the proliferation and activation of T cells
(a) Western blot showed that IOX1 decreased the protein level of PD-L1 in tumor cells
(b) PCR results showed that IOX1 decreased the mRNA level of PD-L1 in tumor cells
(c) Flow cytometry showed that IOX1 promoted the proliferation of T cells
(d) Flow cytometry showed that IOX1 increased the activity of T cells
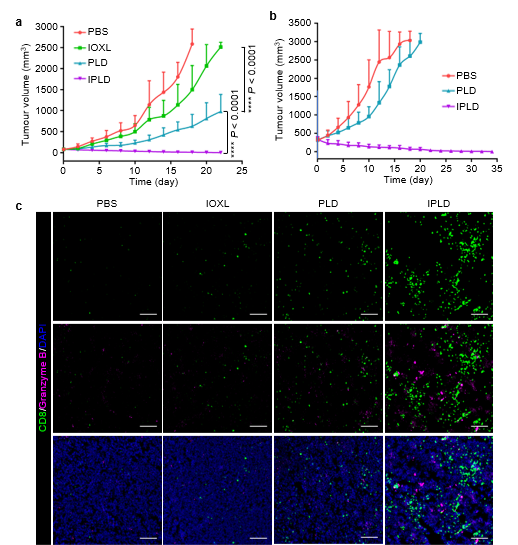
Figure 4: IPLD for CT26 subcutaneous tumor
(a.b) IPLD showed curative effect in small subcutaneous tumor model (initial volume≈ 80 mm3) and large subcutaneous tumor model (initial volume ≈ 350 mm3)
(c) Immunofluorescence photos showed that IPLD treatment increased the infiltration and activity of T cells in tumor tissue of mice.
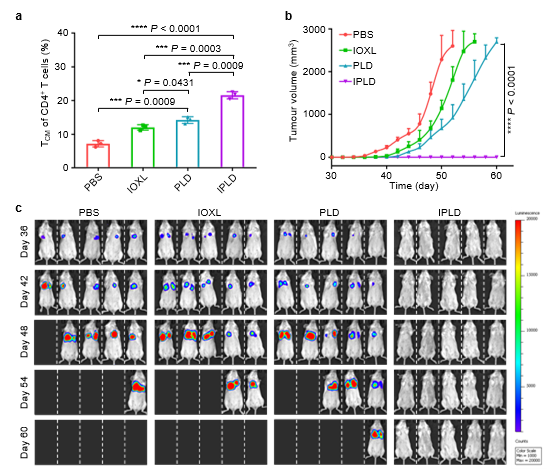
Figure 5: IPLD treatment induces long-term anti-tumor immune memory and resists secondary tumor invasion
(a) After IPLD treatment, the proportion of central memory T cells in spleen of mice increased significantly
(b) The mice treated with IPLD could completely inhibit the growth of subcutaneous tumor
(c) In vivo imaging of small animals showed that the mice treated with IPLD could completely resist the secondary invasion of circulating tumor cells
To sum up, IOX1 through JMJD1A/ β- Catenin signaling pathway reduces the expression of P-gp and PD-L1 in tumor cells, and combines with DOX, which has excellent anti-tumor activity. Compared with PD-L1 antibody, IOX1 has high curative effect and simple structure. In addition, because JMJD1A is only selectively overexpressed in tumor cells, IOX1 can reduce the risk of systemic toxicity during treatment, which provides a new idea for cancer chemotherapy immunotherapy.
To learn more about this article, go to Co-delivery of IOX1 and doxorubicin for antibody-independent cancer chemo-immunotherapy | Nature Communications.
To learn more about Prof. Hong Fan’s research group, go to Youqing shen-Zhejiang University Personal homepage (zju.edu.cn).